Raptor Reliability Simulation Software Software Free Download
EKTS is a simulator for designing electromechanical systems. It allows you to design variety of electromechanical systems using relays, time relays, buttons, motors, switches and some basic mechanical systems. EKTS allows building custom motor circuits using different motor types in different quantities. Main usage of this simulator is aiming at teaching basics of electromechanical systems, therefore it have error pointing feature which shows exact location of error and cause of that produces error.
Other useful feature is listing all used circuit elements for calculating price and defining parts that will be used. EKTS doesn't calculate current flaw and power distribution in through circuit elements therefore it doesn't guarantee having same result in real environment. Version 1.0.3 allows to print all pages and select and drag whole circuit.
RAPTOR is an innovative software designed for accurate protein structure prediction. It combines advanced analysis tools in one integrated software solution and provides three different threading methods. RAPTOR's unique integer programming optimization approach is most effective for finding structure templates of targets with low sequence homology and is able to generate high quality models.
Chertezhi reklamnogo schita dvuhstoronnego. The easy-to-use interface and easy-to-understand E values are ideal for beginners and experts. Above all, the intuitive display of the output enables users to understand the results simply at a glance.
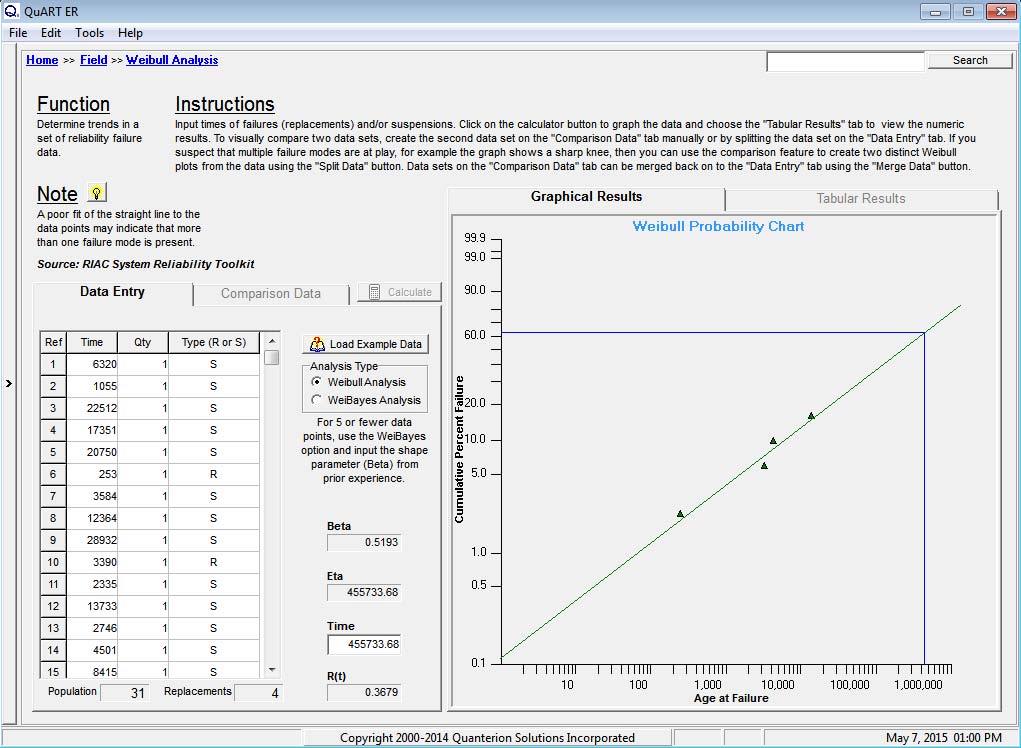
Advanced Specialty Engineering Networked Toolkit (ASENT) 2. Advanced Integrated Maintenance Support System (AIMSS) 3. EAGLE Logistic Support Analysis Record (LSAR). Reliability Software for people looking for Reliability & Maintainability. We offer best Reliability Software like Fault Tree, Monte Carlo, FMECA, Simulation, Reliability. Please complete the form below prior to downloading. Monte Carlo Simulation Software. Raptor: Reliability Simulation Tool.

Given a target protein sequence, if there is a homologous protein with known 3D structure, it can be found by using sequence search tools like PSI-BLAST, also provided in RAPTOR. The target's structure is then built from the known structure; however, when the sequence homology is not significant, i.e. Less than 25%, PSI-BLAST can not come up with a confident hit.
Unlike PSI-BLAST, which simply does a sequence search, protein threading, fold recognition, makes use of both homology and structure information. It scans the protein sequence with an unknown structure against a database of known structures. By using a scoring function and conducting compatibility analysis between three-dimensional structures and linear protein sequences, the best structural template will be identified from which to build the sequence's structure. As a result, protein threading gives a superior prediction than homology modeling when there is marginal sequence homology.